ENG | Raspberry Pi Pico & MicroPython: Code Snippets
Assorted Raspberry Pi Pico MicroPython code snippets.
ENG | Raspberry Pi Pico & MicroPython: Code Snippets
List of uploaded files
1
2
import os
os.listdir()
Example output:
1
['ble_advertising.py', 'ble_simple_peripheral.py', 'main.py', 'source_page_link.txt']
Check hardware
1
2
3
4
5
>>> import sys
>>> sys.platform
rp2
>>> sys.implementation
(name='micropython', version=(1, 24, 1, ''), _machine='Raspberry Pi Pico W with RP2040', _mpy=4870)
Uptime
1
2
3
>>> import time
>>> time.ticks_ms()
652705
I2C scan
1
2
3
from machine import Pin, I2C
i2c = I2C(0, sda=Pin(0), scl=Pin(1))
i2c.scan()
Example output:
1
[68, 118]
Blink built-in LED
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
from machine import Pin
from utime import sleep
pin = Pin("LED", Pin.OUT)
print("LED starts flashing...")
while True:
try:
pin.toggle()
sleep(1) # sleep 1sec
except KeyboardInterrupt:
break
pin.off()
print("Finished.")
Connecting to WiFi from console
1
2
3
4
import network
wlan=network.WLAN(network.STA_IF)
wlan.active(True)
wlan.connect("YourSSID", "YourPass")
Connecting to WiFi and getting time from NTP
This works on Raspberry Pico W (with WiFi/BLE module)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
import network
import ntptime
import time
# Known networks with corresponding passwords
known_networks = {
'Pavel': 'qwerasdf',
'public': "",
}
def sync_time():
print("Synchronizing time via NTP ...")
ntptime.host = "tik.cesnet.cz" # optional
ntptime.settime()
def wifi_try_connect():
wlan=network.WLAN(network.STA_IF)
wlan.active(True)
scanned = wlan.scan()
found = False
for entry in scanned:
ssid_str = entry[0].decode()
if ssid_str in known_networks:
print(f"Found known SSID: {ssid_str}")
found = True
wlan.connect(ssid_str, known_networks[ssid_str])
# Wait a few seconds to see if it connects
print ("Connecting: ", end='')
for _ in range(20):
if wlan.isconnected():
break
time.sleep_ms(500)
print(".", end='')
print()
if wlan.isconnected():
print("Connected successfully.")
return True
else:
if not found:
print("Known wifi connection was not found.")
print("Connection attempt failed.")
return False
if wifi_try_connect():
sync_time()
print(time.localtime())
Example output:
1
2
3
4
5
Found known SSID: U_veverek_2,4
Connecting: ........
Connected successfully.
Synchronizing time via NTP ...
(2024, 12, 22, 15, 8, 54, 6, 357)
Ok, It’s Sunday 2024-12-22 15:12:03. But time is in UTC, I have +1 offset during winter and 6 is day of the week where zero is monday.
BLE (Bluetooth Low-Energy) sensor data broadcast
Also for Raspberry Pi Pico W
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
import time
import bluetooth
import struct
from micropython import const
# BLE event constants
_IRQ_CENTRAL_CONNECT = const(1)
_IRQ_CENTRAL_DISCONNECT = const(2)
# Standard BLE UUIDs for Environmental Sensing
_ENV_SENSE_UUID = bluetooth.UUID(0x181A)
_TEMP_CHAR_UUID = bluetooth.UUID(0x2A6E) # Temperature Characteristic
_HUM_CHAR_UUID = bluetooth.UUID(0x2A6F) # Humidity Characteristic
_PRESS_CHAR_UUID= bluetooth.UUID(0x2A6D) # Pressure Characteristic
# Flags for read and notify
_FLAG_READ = const(0x0001)
_FLAG_NOTIFY= const(0x0010)
# Prepare the GATT server structure
environment_sense_service = (
_ENV_SENSE_UUID,
(
(_TEMP_CHAR_UUID, _FLAG_READ | _FLAG_NOTIFY),
(_HUM_CHAR_UUID, _FLAG_READ | _FLAG_NOTIFY),
(_PRESS_CHAR_UUID, _FLAG_READ | _FLAG_NOTIFY),
),
)
# Advertisement helper for BLE
def advertise(ble, name="PicoW-Env"):
# A simple advertisement for discoverability
# Including flags and name
adv_data = bytearray(
b"\x02\x01\x06" # Flags indicating BLE general discoverable
+ bytes([len(name) + 1, 0x09]) # Complete local name
+ name.encode()
)
ble.gap_advertise(100_000, adv_data)
class BLEEnvSense:
def __init__(self, ble):
self._counter = 0
self._ble = ble
self._ble.active(True)
self._ble.irq(self._irq)
# Holds the connection handle when a central device is connected
self._conn_handle = None
# Create a GATT server and register the Environmental Sensing service
((self._temp_handle, self._hum_handle, self._press_handle),) = self._ble.gatts_register_services((environment_sense_service,))
# Start advertising
advertise(self._ble)
def _irq(self, event, data):
if event == _IRQ_CENTRAL_CONNECT:
# A central connected
conn_handle, addr_type, addr = data
self._conn_handle = conn_handle
elif event == _IRQ_CENTRAL_DISCONNECT:
# A central disconnected
conn_handle, addr_type, addr = data
if conn_handle == self._conn_handle:
self._conn_handle = None
def update_values(self):
# Trial-error fixed point values found values for -12.34C, 43.21% RH, 101325.0Pa
temp_bytes = struct.pack('<i', -1234 + self._counter)
hum_bytes = struct.pack('<i', 4321 + self._counter)
press_bytes= struct.pack('<i', 1013250 + self._counter)
self._counter += 1
self._ble.gatts_write(self._temp_handle, temp_bytes)
self._ble.gatts_write(self._hum_handle, hum_bytes)
self._ble.gatts_write(self._press_handle, press_bytes)
# Notify only if there is a valid connection
if self._conn_handle is not None:
self._ble.gatts_notify(self._conn_handle, self._temp_handle)
self._ble.gatts_notify(self._conn_handle, self._hum_handle)
self._ble.gatts_notify(self._conn_handle, self._press_handle)
def main():
counter=0
ble = bluetooth.BLE()
print("BLE created")
env_sense = BLEEnvSense(ble)
print("BLEEnvSense created")
while True:
# Update BLE characteristics with constants for demonstration
env_sense.update_values()
# Delay before updating again
time.sleep(5)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
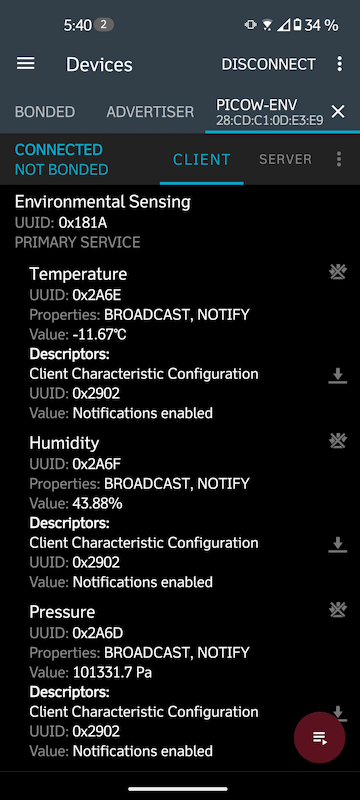 Screenshot of
Screenshot of nRF Connect mobile app
Low-power sleep mode
Raspberry Pi has two funny functions for power saving mode: machine.lightsleep(time_ms) and machine.deepsleep(time_ms). However they have awful side effects:
- Internal RTC clocks stop or significantly slow down - it does matter if you add time stamps to your measurements
- Raspberry Pi Pico still consumes some power so it’s not worth using.
- USB interface is turned off during sleep so you can’t connect to Raspberry Pi Pico. Solution:
- Hold
BOOTSELbutton and reconnect Pico to PC - Download UF2 file from https://github.com/Pwea/Flash-Nuke/tree/main and copy it to Raspberry Pi Pico. It reset and flash gets erased, then it resets again (I think, if not reconnect it again)
- Download MicroPython and upload it to Pico
- Remove lightsleep from Python code and reupload project to Pico in Visual Studio Code
- Hold
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.